Modern workplaces are all about fostering diversity and inclusion not only because they see it as a moral imperative; but also a strategic advantage. Companies that prioritise diversity and inclusion are not only better positioned to attract and retain top talent but also tend to outperform their competitors. However, achieving meaningful progress in this area requires more than just good intentions—it demands the strategic use of advanced HR tools.
Surveys indicate more than 70-80% of job seekers consider diversity and inclusion as important factors when considering job opportunities.
Embracing Diversity and Inclusion
Before delving into the role of advanced HR tools, it’s crucial to understand what diversity and inclusion entail.
Diversity goes beyond traditional markers such as race, gender, and ethnicity; it encompasses a broad spectrum of characteristics, perspectives, and experiences.
Inclusion, on the other hand, involves creating a culture where every individual feels valued, respected, and empowered to contribute their unique insights and talents.
The Challenge of Traditional Approaches
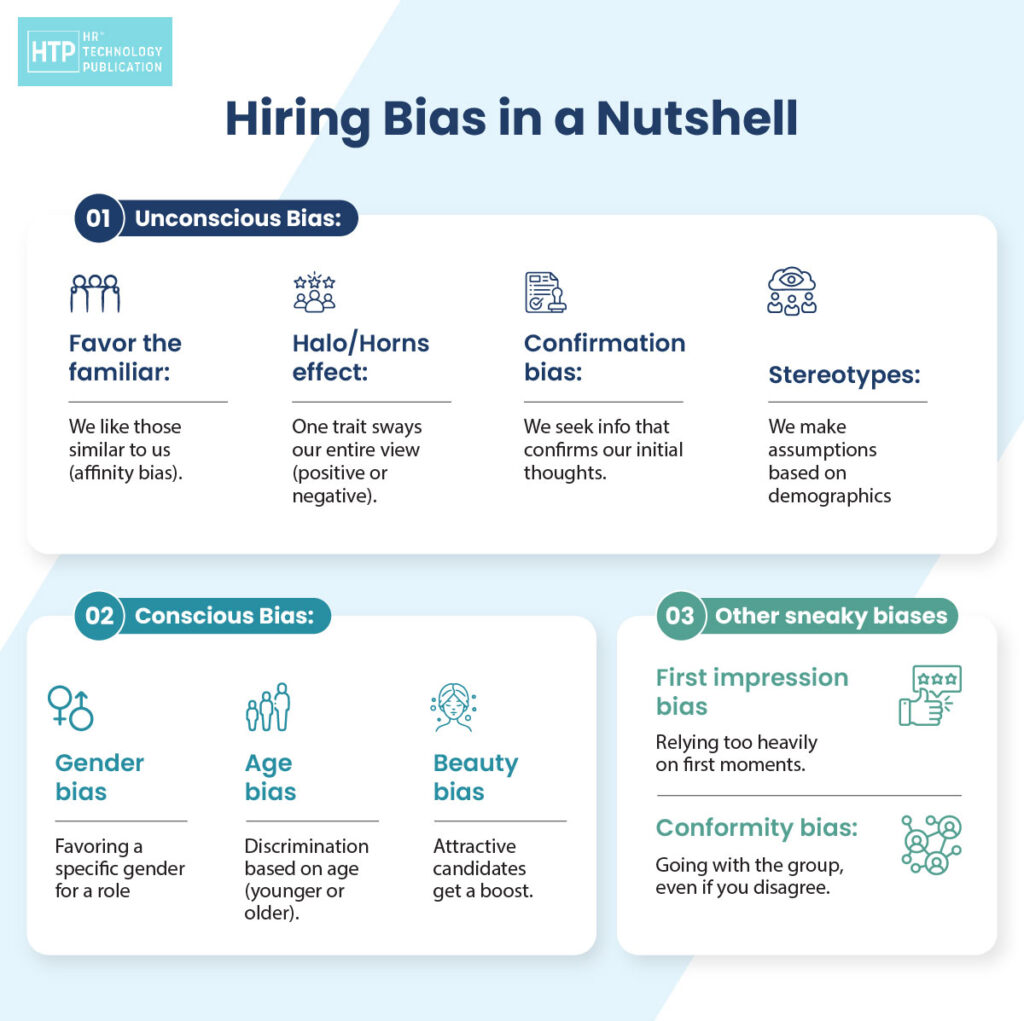
Historically, many organisations have relied on manual processes and outdated methods to address diversity and inclusion. While well-intentioned, these approaches often fall short of driving meaningful change. Without the right tools and technologies, HR teams may struggle to identify and address systemic biases, track diversity metrics effectively, or create inclusive policies and programs.
1. Diverse Hiring Platforms
Advanced recruitment platforms go beyond traditional methods by leveraging AI and machine learning algorithms to address unconscious biases in the hiring process. Here’s a more detailed breakdown of how these platforms work:
- Anonymizing Resumes: These platforms can strip identifying information from resumes, such as names, gender pronouns, and photos, to ensure that hiring decisions are based solely on qualifications and experience.
- Language Pattern Analysis: By analyzing language patterns in job descriptions and applicant resumes, these platforms can identify and flag potentially biased language that may deter qualified candidates from applying.
- Objective Candidate Recommendations: Using objective criteria such as skills, qualifications, and experience, advanced recruitment platforms can recommend diverse candidate pools to hiring managers, helping to ensure a more inclusive hiring process.
2. Inclusive Learning and Development
Learning management systems (LMS) equipped with advanced features play a crucial role in providing equitable learning opportunities for all employees. Here’s how:
- Personalized Learning Paths: Advanced LMS platforms can tailor learning paths to individual employees’ needs, preferences, and learning styles, ensuring that everyone has access to relevant and engaging learning experiences.
- Accessibility Options: These platforms offer accessibility features such as closed captioning, screen readers, and alternative formats for content, making learning materials accessible to employees with disabilities.
- Inclusive Content: Advanced LMS platforms curate and develop content that reflects diverse perspectives, experiences, and backgrounds, fostering a more inclusive learning environment for all employees.
3. Bias Detection and Mitigation
HR analytics tools empower organizations to identify and address patterns of bias in various HR processes. Here’s how these tools work:
- Data Analysis: By analyzing HR data, including performance evaluations, promotion decisions, and compensation practices, these tools can identify disparities and biases that may exist within the organization.
- Identification of Root Causes: HR analytics tools help pinpoint the root causes of bias, whether they stem from systemic issues, unconscious biases among decision-makers, or other factors.
- Targeted Action: Armed with insights from HR analytics, HR professionals can take targeted action to address biases, such as implementing training programs, revising policies and procedures, or restructuring processes to promote fairness and equity.
4. Employee Resource Groups (ERGs) Management
Advanced HR platforms streamline the creation and management of employee resource groups, fostering a sense of belonging and community among employees. Here’s how these platforms support ERGs:
- Centralized Platform: ERG members can use advanced HR platforms as centralized hubs for communication, event planning, resource sharing, and collaboration, making it easier to connect and engage with one another.
- Facilitated Networking: These platforms facilitate networking opportunities for ERG members, helping them build relationships, share experiences, and support each other in their professional development journeys.
- Advocacy and Engagement: ERG leaders can use advanced HR platforms to advocate for inclusion initiatives, raise awareness about diversity-related issues, and engage with senior leadership to drive meaningful change within the organization.
5. Real-Time Feedback Mechanisms
Feedback platforms enable employees to provide anonymous feedback in real time, creating channels for voicing concerns, reporting incidents of bias or discrimination, and offering suggestions for improvement. Here’s how these platforms work:
- Anonymity: By allowing employees to provide feedback anonymously, these platforms create a safe space for sharing candid thoughts and experiences without fear of retaliation or judgment.
- Timely Insights: Real-time feedback platforms provide HR teams with timely insights into employee sentiments, allowing them to address issues promptly and proactively.
- Continuous Improvement: By soliciting feedback on an ongoing basis, organizations can continuously identify areas for improvement and take action to create a more inclusive and supportive work environment for all employees.
By leveraging advanced HR tools in these key areas, organizations can proactively address barriers to diversity and inclusion, create more equitable workplaces, and foster a culture where every individual feels valued, respected, and empowered to succeed.
Conclusion
In the quest to build diverse and inclusive workplaces, advanced HR tools are indispensable allies. By harnessing the capabilities of technology, organisations can overcome the limitations of traditional approaches and drive meaningful change. However, it’s important to remember that technology alone is not a panacea—effective diversity and inclusion efforts require commitment, leadership buy-in, and ongoing collaboration across all levels of the organisation. By leveraging advanced HR tools in conjunction with strategic initiatives and a culture of inclusivity, companies can create environments where every individual feels valued, empowered, and able to thrive.



